Blog
Product Development
Here I expand on some of the elements of a typical product design project structure.
Concept generation
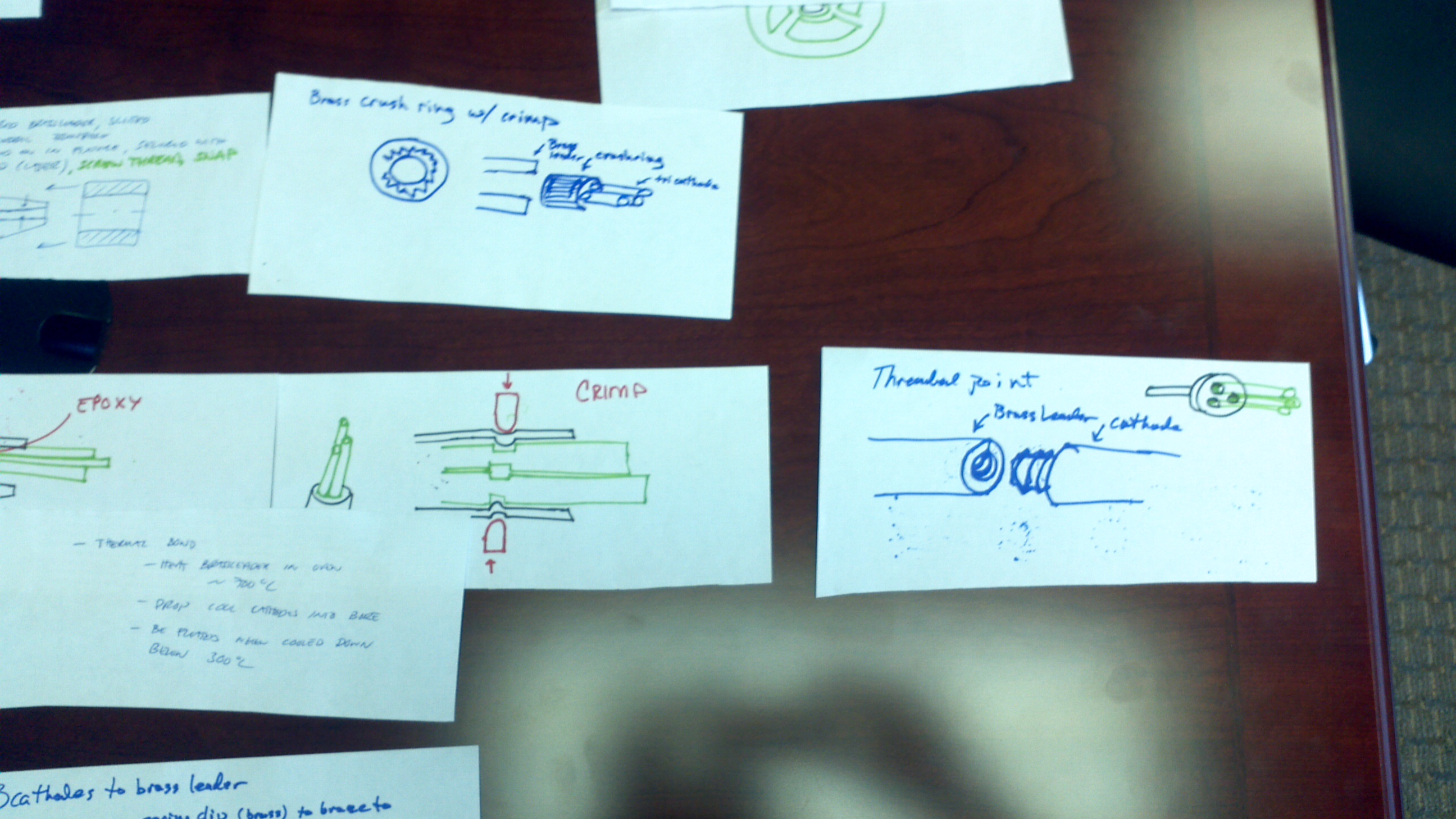
The goal is to quickly produce and capture a diverse quantity of ideas. That could be a simple form, feature, or even a phrase. Typical activities include brainstorming and quick sketching.
Concept generation is a set of learned skills that are refined with practice. It requires you to release the urge to critique or analyze so that you can freely produce one thought after another. Groups often benefit from a mediator to guide sessions.
Once the flow of new ideas begins to diminish you can step back to organize, analyze, and filter the data.
Mechanical sketching
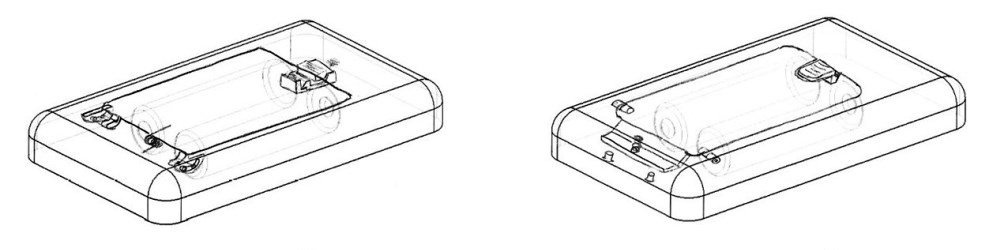
During concept generation sketches are typically quick and rough approximations of an idea. You would rather document the concept and move on to the next instead of spend time refining. After a session is over and concepts have been filtered, candidate concepts are sketched in more detail. Sometimes a more detailed sketch is required to verify feasibility. Commonly a concept will look promising as a cross section or thumbnail but will fall out when considering all three dimensions or drawing the concept truevto scale.
Product research
Product research is a part of the education phase. When taking on any new problem you must familiarize yourself with the objectives and constraints as well as other information including solutions to similar problems. Research can include:
- Similar products made by the same company
- Similar products made by others in the industry
- Similar products made for other industries
- Different products that solve a similar problem
- Technical reference material (standards, literature, etc)
Research can be done before or after concept generation. The knowledge you acquire during research will color your performance during concept generation. You choose to do it before, after, or both depending on your project strategy.
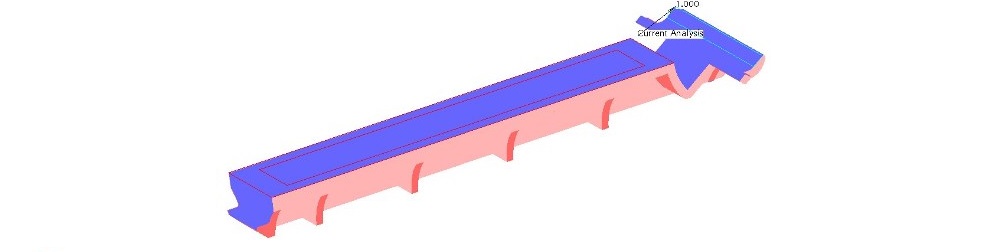
Part design
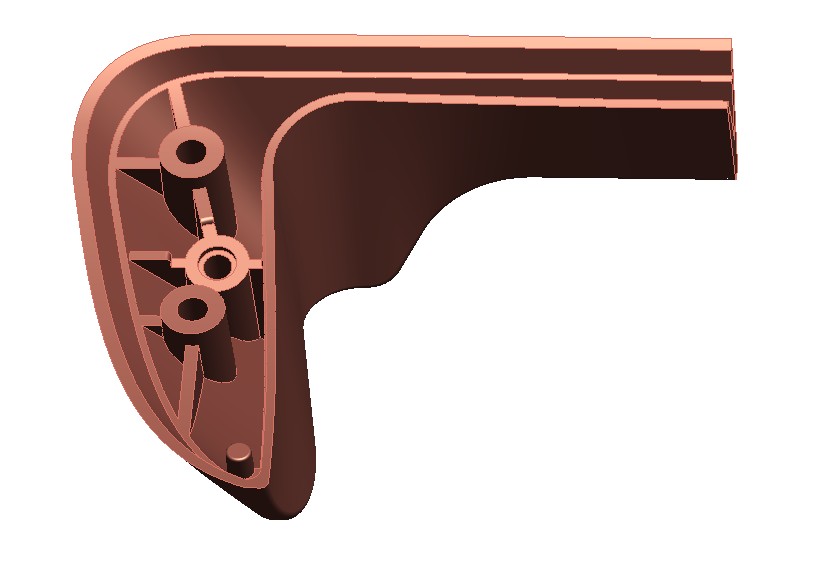
Part design is a blanket term relating to the process of forming features and geometries to produce a component which functions according to its requirements. It is often combined with one or more analyses in an iterative cycle of refinement.
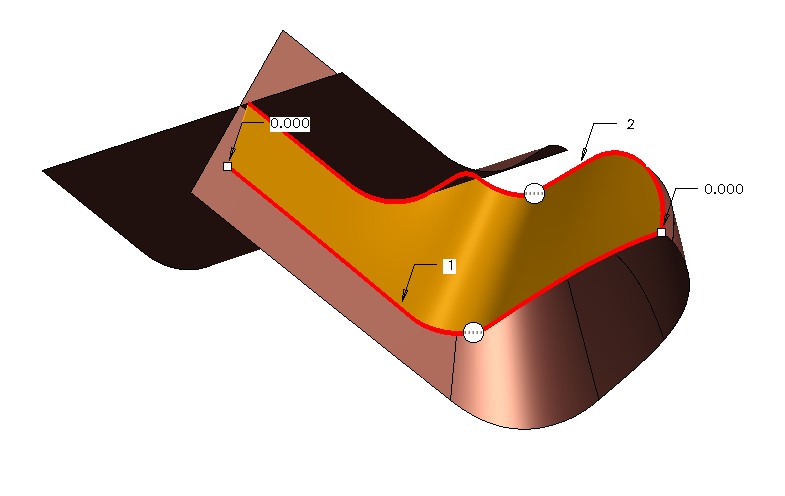
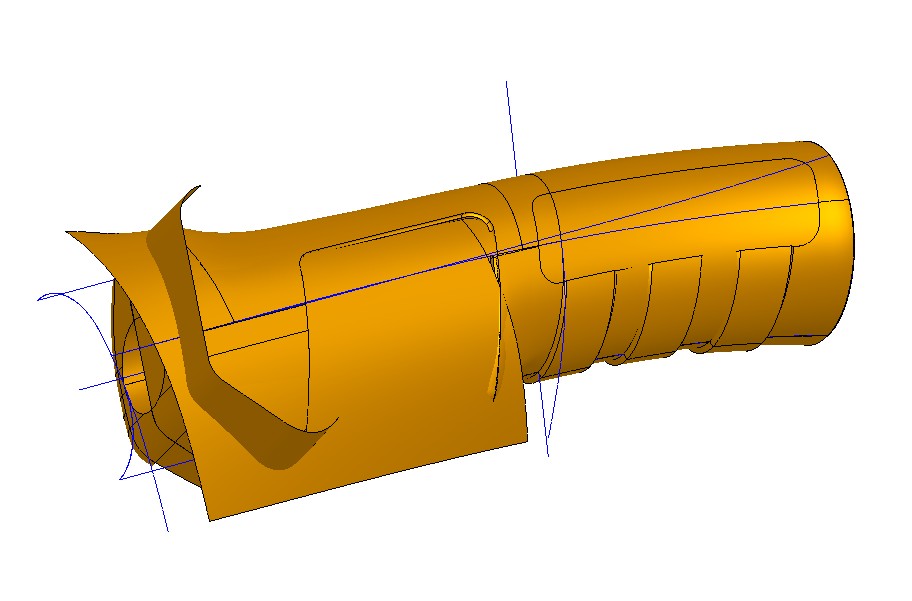
Advanced surfacing
Generating features from high quality and complex surfaces requires advanced methods. Often several control curves need to be created as references to define boundaries and curvature.
Top down Master models
Some parts share common geometry. They may be mirrored, be halves of the same overall shape, or interface with another component (ie. screws). One method for creating parts like this is to construct a master model describing the overall geometry. Then, that geometry (or part of it) is shared or copied at the beginning of a child part. The parts remain associated so that if the master geometry is modified the changes will propagate through to the children.
Engineering prototypes and testing
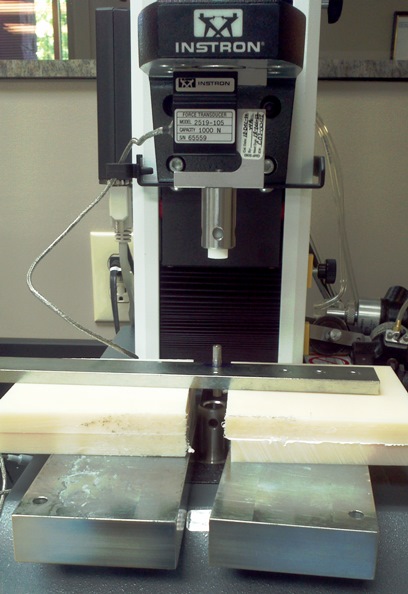
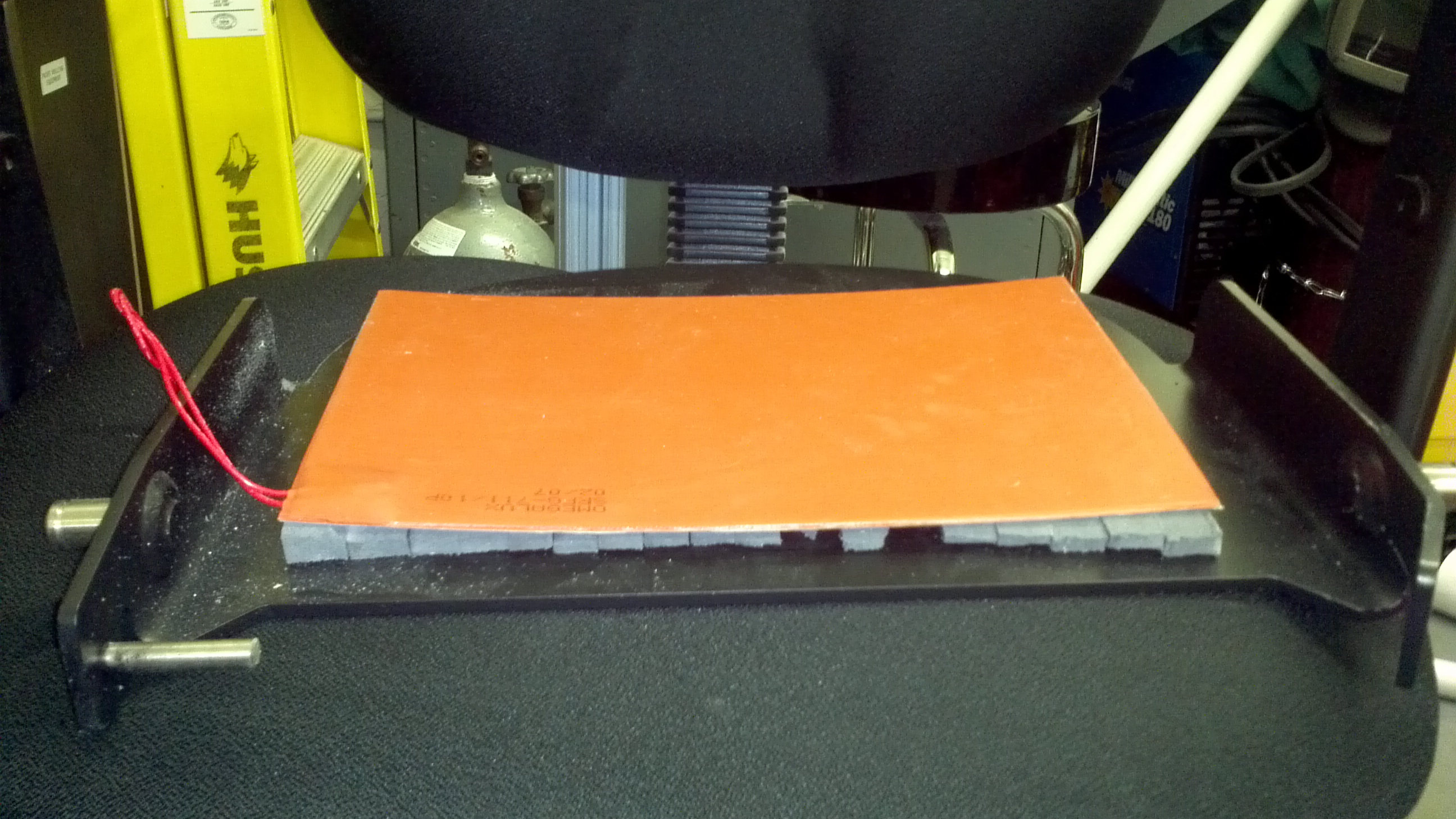
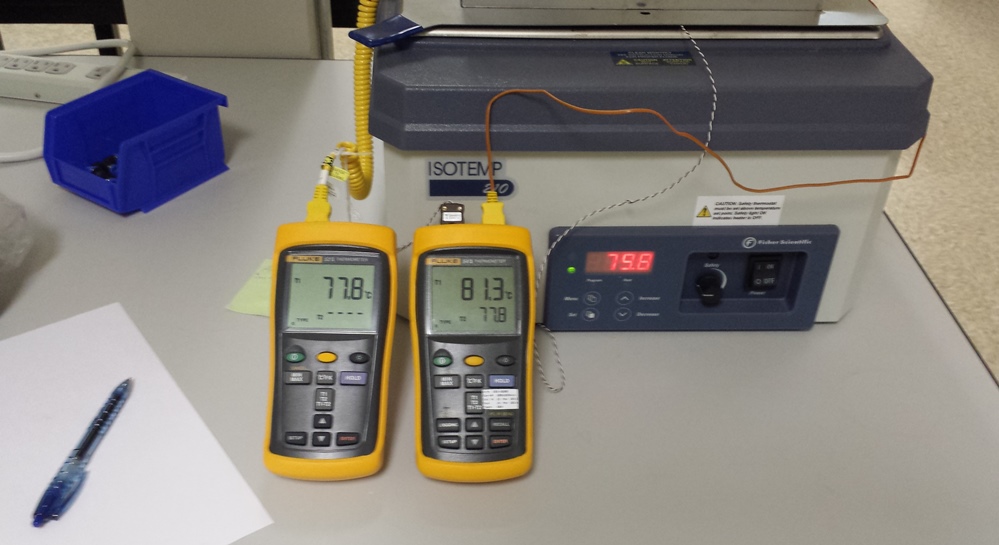


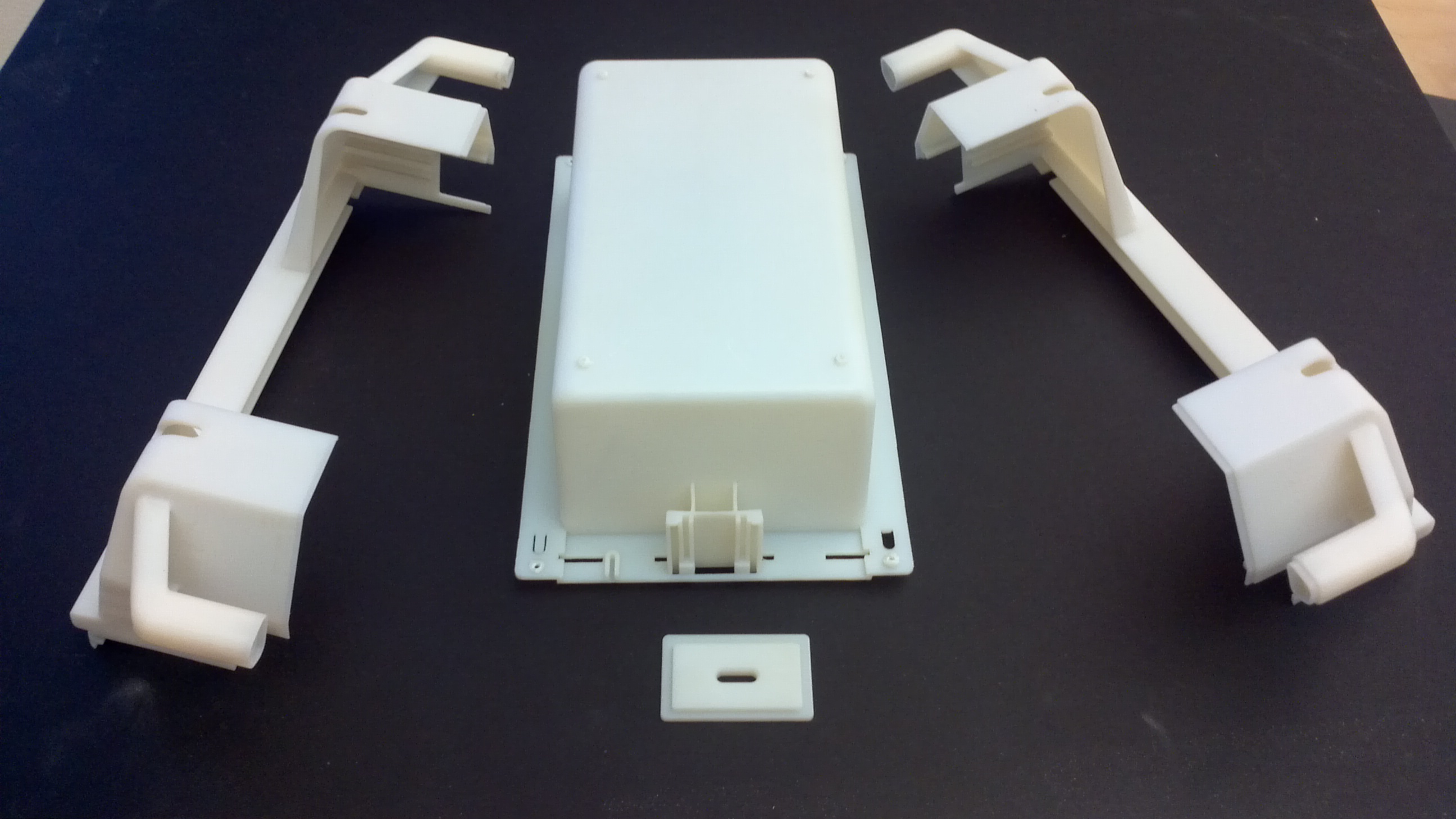

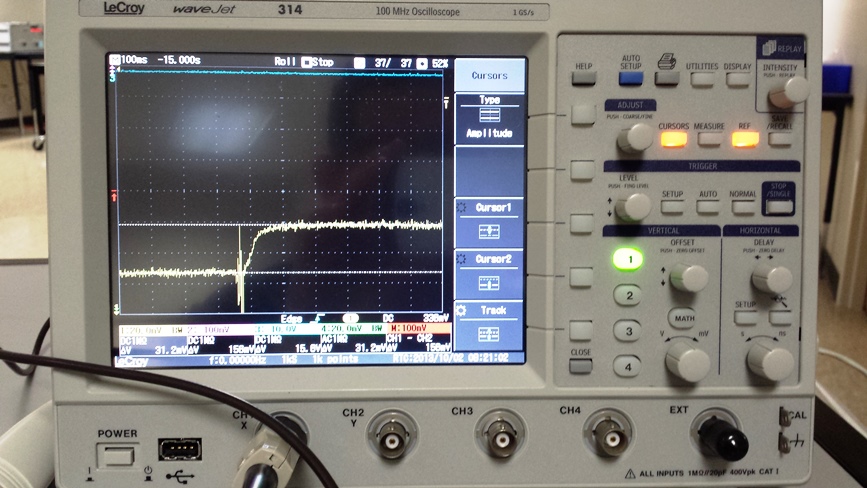
Engineering analysis
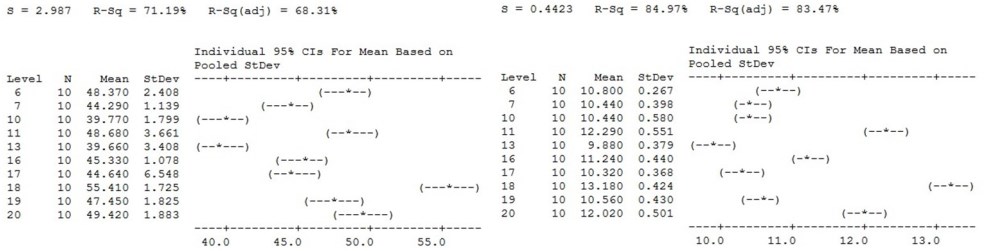
Statistical analysis of results using software like Minitab.
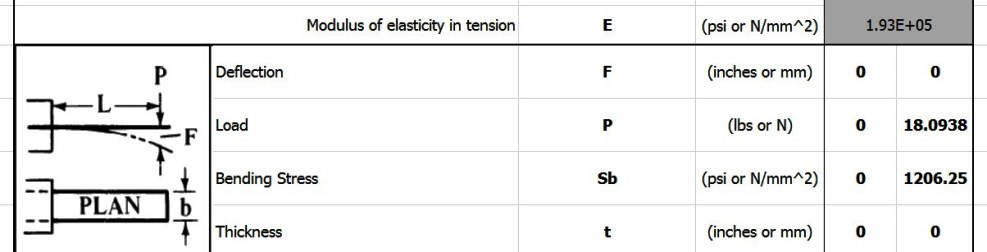
Engineering calculations using Excel
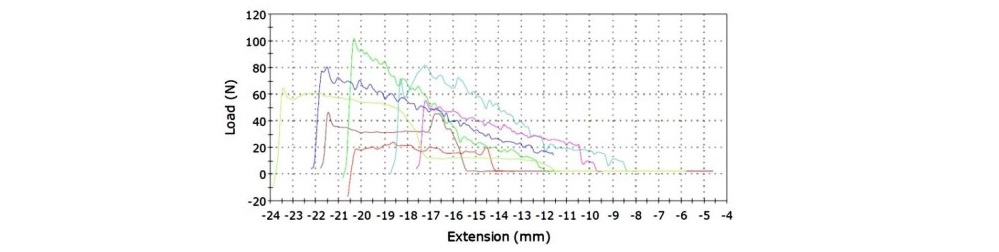
Test results